
If you have a sore throat that isn’t going away, you may have strep throat. Strep throat is very contagious, and you can easily spread it to your friends and family.
The good news is that it can be gone within several days with the right treatment. Keep reading to learn more about whether you should go to an ENT for strep throat.
What is Strep Throat?
Strep throat refers to an infection in your throat and tonsils. Tonsils are the two fleshy masses at the back of your throat, one on each side.
Strep throat is caused by a type of bacteria called group A streptococcus. It causes inflammation and a sore throat.
When you have strep throat, your throat may feel sore and scratchy. While it’s most common in children, anyone can get it.
What are the Symptoms of Strep Throat?

Symptoms of strep throat typically appear 2 to 5 days after exposure and can include:
- Throat pain that comes on quickly
- Red, swollen tonsils, sometimes with white patches
- Pain when swallowing
- Red spots on the roof of the mouth
- Swollen, very tender lymph nodes in the neck
- Headache
- Body aches
- Rash
- Loss of appetite
- Abrupt fever of 101°F or higher
- Nausea or vomiting
How Does Strep Throat Spread?
Strep throat is highly contagious. Some people with strep throat don’t exhibit symptoms or appear unwell but can still pass it on.
However, those with symptoms or who appear ill spread it more quickly. The bacteria responsible for strep throat can be spread by nasal or oral droplets and secretions of an infected person.
You can get strep throat if you:
- Share utensils with an infected individual
- Inhale tiny droplets from an infected person’s sneeze or cough
- Touch a surface with secretions or droplets, and then touch your nose or mouth
Should You Go to an ENT for Strep Throat?
If you experience symptoms of strep throat, consult your doctor promptly for a timely diagnosis and treatment. Strep throat doesn’t go away on its own.
Without treatment, it can also cause rheumatic fever, a serious condition that can permanently damage your heart valves and muscles. Other complications of untreated strep throat include:
- Ear infections
- Sinusitis
- Abscesses around the tonsils
- Scarlet fever
- Pneumonia
- Inflammatory arthritis
- Meningitis
- Blood poisoning
- Kidney inflammation
- Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome, a potentially life-threatening bacterial infection
How is Strep Throat Diagnosed?
During your visit, you’ll undergo a physical exam. Your ENT specialist will also ask about your symptoms.
If they suspect you have strep throat, they may order a throat culture or rapid antigen test.
Rapid Antigen Test
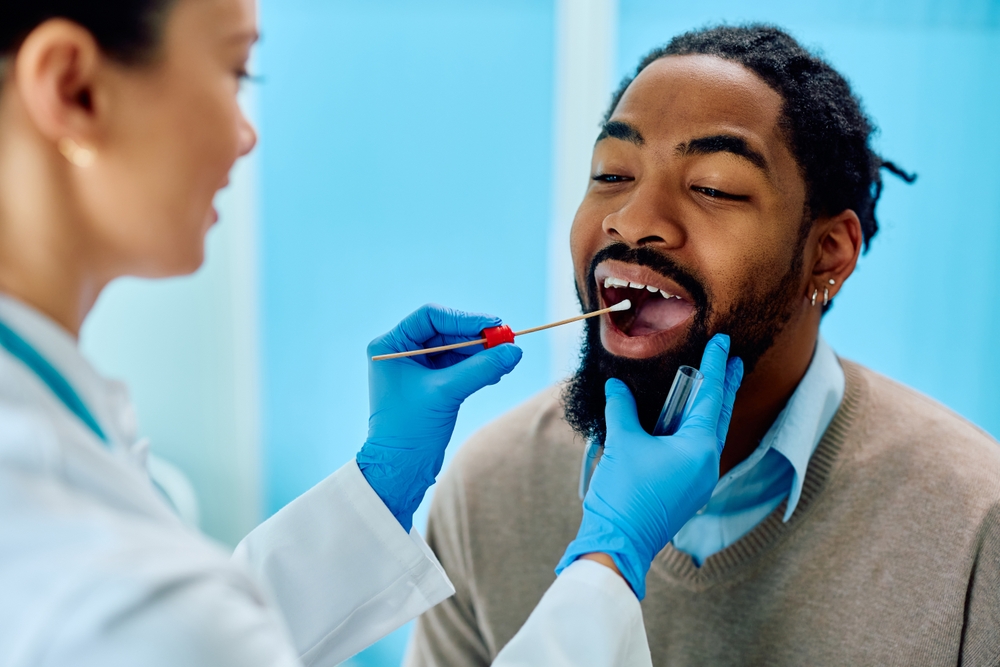
A rapid antigen test determines whether your sore throat is a result of a strep infection. For this test, a swab sample is collected from your throat.
The sample is tested with a kit to check for strep bacteria. The results are ready in about 5 minutes.
If the test is positive, you have strep throat, and no additional tests may be required. If it’s negative, but your ENT specialist still suspects strep throat, they may perform a throat culture to confirm the diagnosis.
Although the rapid test is usually reliable, it can sometimes miss an infection.
Throat Culture
Samples obtained from the back of your throat and tonsils are cultured in a laboratory to detect the presence of strep bacteria. The results of a throat culture may take up to 2 days to be reported.
A throat culture may find strep bacteria that the rapid antigen test missed.
How is Strep Throat Treated?
If you’re diagnosed with strep throat, your ENT specialist may prescribe antibiotics such as amoxicillin or penicillin to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Antibiotics are usually taken for 10 days.
Follow your ENT doctor’s instructions, including finishing your course of antibiotics, even if you feel well. The bacteria can still be present even when you’re feeling better.
Not taking your antibiotics as directed could trigger a relapse or lead to antibiotic resistance. On the other hand, completing the entire course of medication will eliminate the bacteria and prevent complications.
Your fever should subside within a day. In about 2 to 3 days, other symptoms will also begin to resolve.
If you don’t feel any better after 1 to 2 days of starting treatment, contact your ENT specialist.
What At-Home Remedies Ease Strep Throat?
The following at-home tips can help you feel better while antibiotics and your immune system work together to combat strep throat.
Take Ibuprofen
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen can help alleviate throat pain, inflammation, and fever. Be sure to follow the dosage instructions and consult your ENT specialist before taking any new medications.
Eat Soft Foods
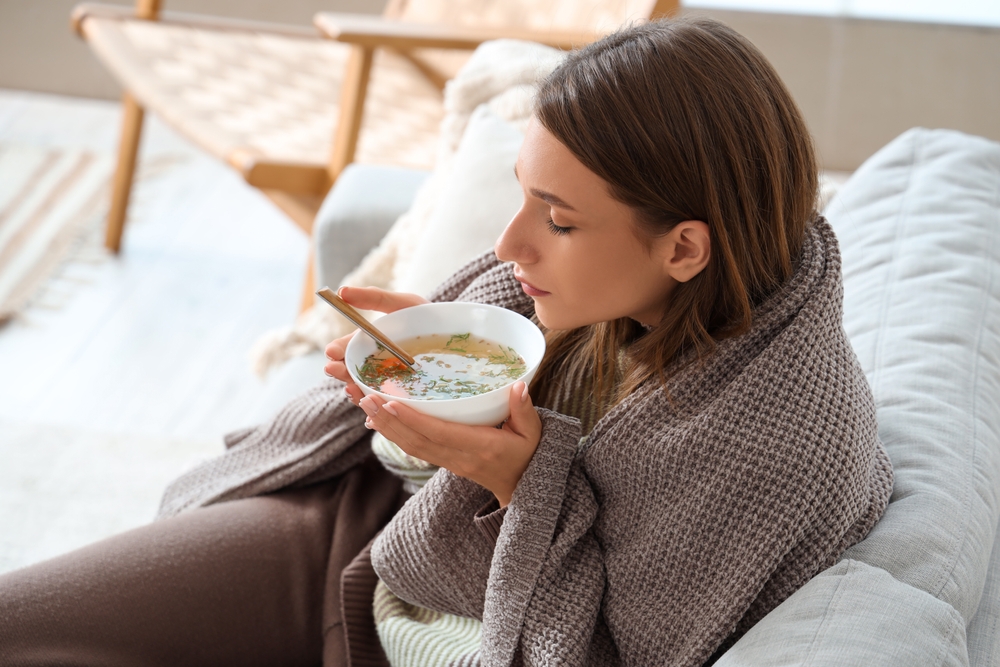

Eat foods such as applesauce, mashed potatoes, yogurt, oatmeal, scrambled eggs, and cream-based soups that have soft textures and are easy on your throat. They’ll keep you nourished without irritating your sore throat further.
Avoid hot drinks and spicy, rough-textured, dry, acidic, and hot foods that are hard to swallow and can worsen pain and inflammation in your throat.
Gargle Salt Water
Gargling with warm salt water a few times daily can help ease the discomfort and swelling associated with strep throat. To make your solution, add ¼ or ½ teaspoon of salt to about 8 ounces of warm water.
Stir to dissolve the salt. Gargle the saltwater in the back of your throat and then swish it around your mouth before spitting it out.
Get Plenty of Rest
Ensure you’re getting enough rest while recovering from strep throat. Sleep helps your immune system fight infections more effectively, helping you feel better sooner.
Get Rid of Your Strep Throat
At Southern Indiana ENT, our ear, nose, and throat specialists can diagnose and treat your strep throat to alleviate your symptoms, ensure complete recovery, and prevent complications.
Do you have symptoms of strep throat? Schedule your appointment at Southern Indiana ENT in Indianapolis, IN, to get an accurate diagnosis and prompt, effective treatment.

